You're here: Main page > 2.2.1.3. Historic trolleybuses > Articulated trolleybuses of the Hungarian type Ikarus 280.93
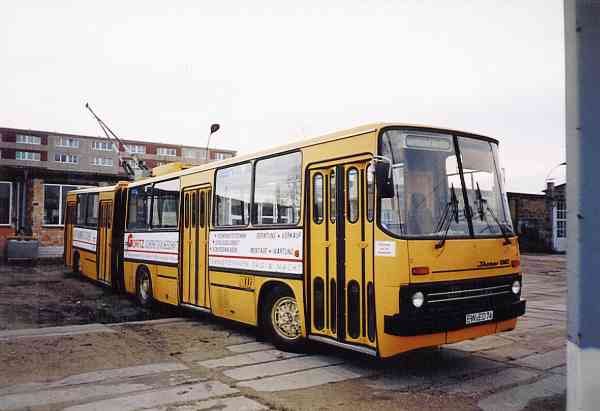
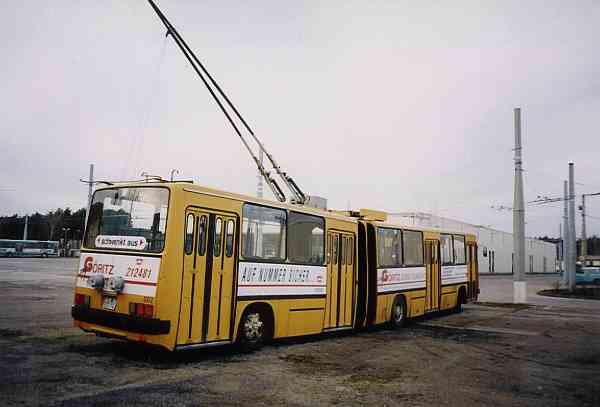
Articulated trolleybuses of the Hungarian type Ikarus 280.93

The articulated trolleybuses of the Hungarian type Ikarus 280.93 were manufactured by Ikarus
in Budapest/Hungary. The GANZ factories Budapest/Hungary supplied the electrical equipment of
the trolleybuses.
The trolleybus is a three-axle vehicle. The A (first) and C (third) axles steer, and
the vehicle is propelled by the B (second) axle.
The vehicle has 4 doors. The doors are electrical-pneumatically actuated. For security, when
the doors are closed 4 door control lights light up. The doors are opened and closed by the
driver.
Now a few technical data:
| Vehicle length |
16500 |
mm |
| Vehicle length with current collectors |
17815 |
mm |
| Vehicle width |
2500 |
mm |
| Vehicle height |
3250 |
mm |
| Vehicle weight unloaded |
13950 |
kg |
| Admissible total vehicle weight |
23860 |
kg |
| Axle load in front |
6600 |
kg |
| Axle load centre |
17260 |
kg |
| Axle load in the back |
6600 |
kg |
The trolleybus is equipped with a 600 V-high voltage system as well as a 24 V-low voltage
system that every other commercial motor vehicle also has.
The vehicle is propelled by an electric motor with 196 kW performance by 2300 rpm. The
electrical driving motor is designed for a nominal voltage of 600 V direct current. The
electric motor receives the driving power over 2 current collectors from the overhead lines
system. The right-sided current collector must always be in contact with the negative wire, and
the left-sided current collector must always be in contact with the positive wire. The
current
collectors are attached on a framework on the trailer roof. This arrangement allows the
trolleybus to drive (during parallel travel) up to 4,5 m to either side of the overhead lines.
The driving motor is controlled via a direct current chopper. The direct current chopper is an
electronic system, which enables an infinitely variable (pulse width) application of the
voltage to the driving motor. It sends the voltage of the overhead line with a lasting
frequency impulse-like to the drive motor. If the width of the impulses are modified, the
voltage of the drive motor can be infinitely variable regulated. The inserted direct current
chopper has several functions. Except the regulation of the armature current of the drive
motor
at large rate also the reduction of the energizing current is made by a thyristor (so-called
field attenuation). The vehicle use the common thyristor type impulse control. The circuit is
executed in such a way that when braking the drive motor operates as generator and back-feeds
electricity into the overhead line. The vehicle has also a partial or full power regeneration
during electrodynamic braking.
The vehicle achieves a maximum speed of 65 km/h.
The tire size 11.00-20 16 PR or 11.00R20 16 PR is used.
The vehicle has 36 seats inclusively driver's seat and the maximum number of passenger related
to the vehicle useful area is 110.
The vehicle has an electrical auxiliary engine. This propels the compressor, the hydraulic
pump of the guidance assistance as well as the 24 V-generator.
The vehicle is equipped with air cushions. There are 2 air cushions at A- and C-axles, and 4
air cushions at B-axle. The air cushions are adjusted to 350-mm +/-10 mm between roadway and
car lower edge.
In the comparison with the ÖAF-Gräf & Stift NGE 152 the Ikarus 280.93 has pro and
cons, however in the direct comparison does not necessarily fare badly.
Advantages:
- guidance assistance also functions while stationary
- pneumatic cushions cushioning also strong roadway unevenness softly
- very agilely due to the guided C-axle
- driver sits high over the roadway and has thereby better vision
- vehicle very durable, small susceptibility to interference
- vehicle has few seats to seat the passengers more comfortably
Disadvantages:
- door closing mechanism does not have security to prevent the passenger from being gripped
when getting on or off (if the driver overlooks a passenger, that is very fatal)
- driver must open and close doors
- the ventilation and blowers for heating are very noisy
- no auxiliary engine, when the current supply is interrupted the vehicle fails
- when driving along curves the trailer swings out strongly
- the floor very high and to achieve over three levels (for older passengers difficult
stepping
in and out)
- drive motor relatively loud